Lahore’s Artificial Rain for Cleaner Air
Lahore, a city historically entangled in pervasive air quality concerns, recently underwent a monumental transformation in its fight against pollution. A groundbreaking initiative introduced artificial rain, marking a pivotal moment in the relentless battle against environmental degradation. This article delves into the profound significance of this innovative approach and its far-reaching implications for Lahore’s persistent pollution issues.
Historical Context of Lahore’s Pollution Woes:
For years, Lahore has grappled with alarmingly high pollution levels, consistently earning its place among the world’s most polluted urban centers. The city’s atmosphere has been burdened with smog, affecting the health and well-being of its inhabitants. However, recent developments offer a glimmer of hope in this struggle.
The Game-Changing Initiative:
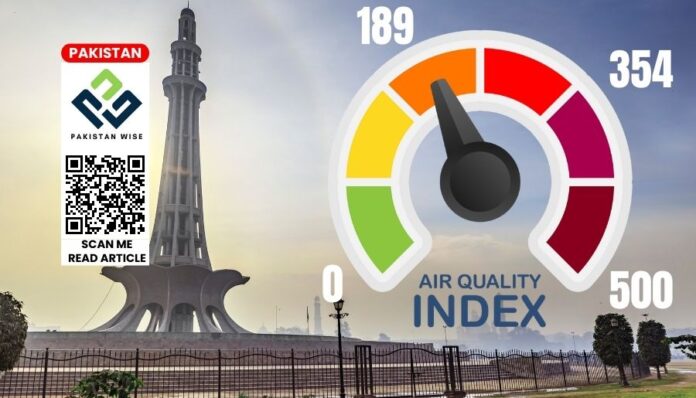
In a pioneering move, Lahore initiated a trial that yielded promising results in dispelling the persistent smog. Notably, the Air Quality Index (AQI) plummeted from a staggering 354 to a significantly improved 189, offering tangible evidence of the initiative’s success.
The Mechanism: Cloud Seeding
The city orchestrated this transformation with the aid of specialized aircraft from the UAE, employing a technique known as cloud seeding. This method involves the introduction of substances like salt flares into clouds, stimulating the formation of raindrops or snowflakes. By harnessing this weather manipulation technique, Lahore aimed to combat air quality deterioration effectively.
Execution and Impact
Mohsin Naqvi, the Caretaker Chief Minister of Punjab, oversaw the deployment of 48 strategically positioned flares near Shahdara and Muridke. This trial extended across ten different sites within the city, effectively demonstrating the potential efficacy of artificial rain in combating pollution.
Significance Beyond Lahore’s Boundaries:
Lahore’s successful trial of artificial rain stands not only as a local triumph but also as a beacon of hope in the broader context of environmental challenges. Cloud seeding, as demonstrated in this initiative, emerges as a viable solution not just for Lahore but for regions globally grappling with similar environmental crises.
Table: Before and After AQI Stats
| Locations | Before AQI | After AQI |
|---|---|---|
| Shahdara | 354 | 189 |
| Muridke | 354 | 189 |
| Other Locations | – | 189 |
This groundbreaking step towards leveraging technology for environmental betterment stands as a testament to the potential of innovative solutions in addressing persistent challenges. As Lahore continues to evolve and adapt, the successful integration of artificial rain offers a promising blueprint for other cities striving to overcome similar environmental adversities.
Conclusion:
The implementation of artificial rain in Lahore represents a paradigm shift in combating pollution. This innovative approach not only showcases the city’s commitment to tackling environmental issues but also underscores the potential of such methods in creating cleaner and healthier urban spaces worldwide.